Search Engine Optimization Latest 2022
What is Search Engine Optimization (SEO)?
Formal Definition-
Search engine optimization is a set of technical and content practices aimed at aligning a website page with a search engine’s ranking algorithm so it can be easily found, crawled, indexed, and surfaced in the SERP for relevant queries.
A simpler definition of SEO:
SEO is about making improvements to your website’s structure and content so its pages can be discovered by people searching for what you have to offer, through search engines.
The simplest definition of SEO:
SEO is what you do to rank higher on Google and get more traffic to your site.
Yes, Google is just one search engine of many. There’s Bing. Directory search engines. Even Instagram is a search engine. But capturing 92% of the market share, the terms “Google” and “search engine” are synonymous for the intents and purposes of this post.
Benefits & importance of Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
People are searching for any manner of things both loosely and directly related to your business. These are all opportunities to connect with these people, answer their questions, solve their problems, and become a trusted resource for them.
More website traffic: When your site is optimized for search engines, it gets more traffic which equates to increased brand awareness, as well as…
More customers: To get your site optimized, it has to target keywords—the terms your ideal customers/visitors are searching—meaning you’ll get more relevant traffic.
Better reputation: Ranking higher on Google builds instant credibility for your business. If Google trusts you, then people trust you.
Higher ROI: You put money into your website, and into the marketing campaigns that lead back to your website pages. A top-performing site improves the fruits of those campaigns, making your investment worth it.
Types of Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Google and other search engines take several factors into account when ranking content, and as such SEO has many facets. The core three types of SEO are on-page, off-page, and technical SEO:
On-page SEO: Optimizing the quality and structure of the content on a page. Content quality, keywords, and HTML tags are the key players for on-page SEO.
Off-page SEO: Getting other sites, and other pages on your site to link to the page you are trying to optimize. Backlinks, internal linking, and reputation are your off-page MVPs.
Technical SEO: Improving your site’s overall performance on search engines. Site security, UX, and structure are key here.
The above three types of SEO are used for websites and blogs, but they also apply to three subtypes of SEO:
Local SEO: Getting your business to rank as high as possible in Google Maps and on the local results of the SERP. Reviews, listings, and Google Business profile optimization are most important here.
Image SEO: A mix of on-page and technical strategies to get images on your website pages to rank in Google image search.
Video SEO: A mix of on-page, technical, and off-page strategies to get your videos to rank in YouTube or Google video results.
While all three subtypes require all three core types of SEO, they do vary in how heavily they rely on each core type.

How does Search Engine Optimization (SEO) work?
So how does Google determine which pages to surface in the search engine results page (SERP) for any given query? How does this translate into traffic to your website? Let’s take a look at how SEO works.
Google’s search crawlers constantly scan the web, gathering, categorizing, and storing the billions of web pages out there in its index. When you search for something and Google pulls up results, it’s pulling from its index, not the web itself.
Google uses a complex formula (called an algorithm) to order results based on a number of criteria (ranking factors—which we’ll get into next) including the quality of the content, its relevance to the search query, the website (domain) it belongs to, and more.
How people interact with results then further indicates to Google the needs that each page is (or isn’t) satisfying, which also gets factored into the algorithm.
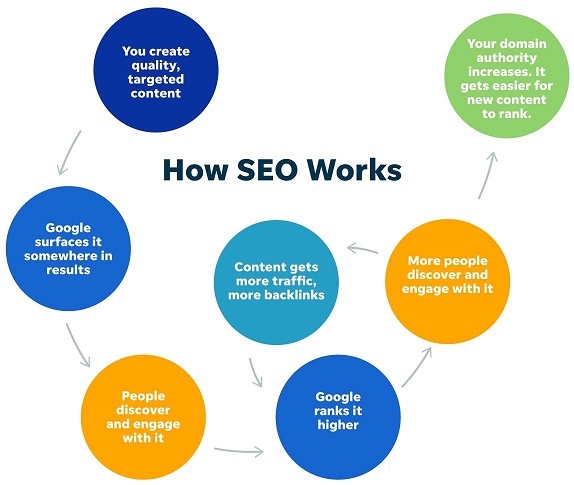
In other words, SEO works like a complex feedback system—to surface the most accurate, trustworthy, and relevant results for any given search using input from you, Google, and searchers. Your role is to produce content that satisfies Google’s expertise, authority, and trust requirements (E-A-T), which satisfy its searchers’ requirements.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) ranking factors on Google
So what are those requirements? What actually constitutes quality, targeted, EAT-friendly, and SEO-optimized content? Well, there are hundreds of Google ranking factors, and Google is also constantly evolving and refining its algorithm to continue providing the best experience possible, but there are 12 that should be prioritized.
According to FirstPageSage, these are the top Google ranking factors and how they are weighted:
Consistent publication of high-quality content (26%)
Keywords in meta title (17%)
Backlinks (15%)
Niche expertise (13%)
User engagement (11%)
Internal links (5%)
Mobile-friendly/mobile-first (5%)
Page speed (2%)
Site security/SSL certificate (2%)
Schema markup/structured data (1%)
Keywords in URL (1%)
Keywords in H1 (1%)
But make no mistake about the factors at the bottom of this list. As you can see in the below chart, “Other” factors, like unlinked mentions, social signals, domain history, outbound links, and site structure, carry 1% weight.
But given that there are at least 200 Google ranking factors; that’s at least 189 “other” factors that collectively make up that 1%. In other words, those seemingly small factors, like keywords in URL, that on their own make up 1%, are not so small.
How to do SEO: On-page optimization
Now it’s time to talk about how to actually do SEO—how to optimize your website for these factors so you can rank higher on Google and get more traffic. This requires a combination of on-page, off-page, and technical optimizations, so we’re going to organize the steps in that manner. Here are your on-page optimization steps:
Start with keyword research
Create quality content targeting those keywords
Place your keywords
Optimize your titles
Optimize your meta descriptions
Include and optimize images
Internal and external links
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Tools
You can’t carry out effective search engine optimization without data, and to get data, you need tools. Luckily, most of them are free. The best SEO tools for an optimal SEO strategy are:
Google Analytics: This is the gold standard for website traffic analytics, and it’s free. Use it for any and all SEO metrics to measure your performance, such as traffic, time on page, engagement with page, number of pages per session, and (lots) more.
Google Search Console: GSC is essential for content-focused and technical SEO. Although some Search Console data appears in Google Analytics, there is a lot you get in the platform on its own. Use it for Core Web Vitals, granular query analyses, indexing, and more.
Keyword research tools: As mentioned above, you’ll need these so you can find keywords that are realistic for you to target in terms of search volume and competition. Use my roundup of the best paid and free keyword research tools to find the right one for you.
SEO software: If you’re going to look at deeper SEO metrics like backlinks, competitive information, and more advanced keyword data, you’ll need a paid SEO tool like Ahrefs, Moz Pro, Screaming Frog, SEMrush, etc. Some of these offer free trial versions or free services for the first 500 (or something) links.
Website graders: Whereas the aforementioned tools are often complex and require you to know how to make sense of the data, website graders can simplify SEO for you and offer more guidance.
Read More About Technology Risk
Buy From Amazon
