IaaS Latest 2022
What is IaaS?
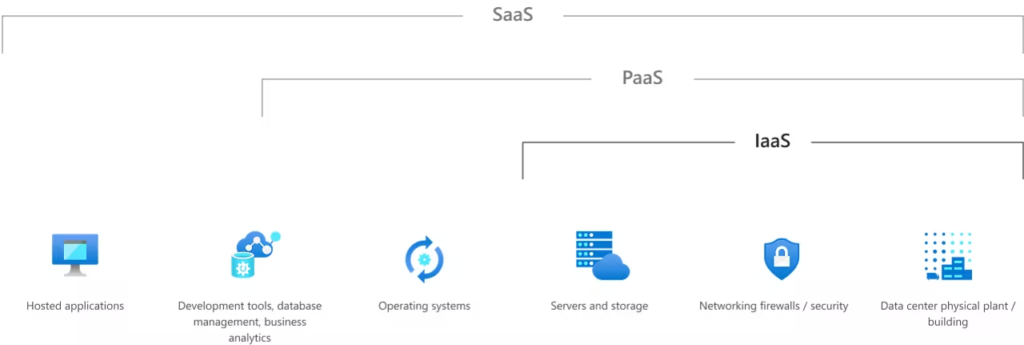
IaaS (Infrastructure as a service) is a type of cloud computing service that offers essential compute, storage, and networking resources on demand, on a pay-as-you-go basis. IaaS is one of the four types of cloud services, along with software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and serverless.
Migrating your organization’s infrastructure to an IaaS solution helps you reduce maintenance of on-premises data centers, save money on hardware costs, and gain real-time business insights. IaaS solutions give you the flexibility to scale your IT resources up and down with demand. They also help you quickly provision new applications and increase the reliability of your underlying infrastructure.
IaaS lets you bypass the cost and complexity of buying and managing physical servers and datacenter infrastructure. Each resource is offered as a separate service component, and you only pay for a particular resource for as long as you need it. A cloud computing service provider like Azure manages the infrastructure, while you purchase, install, configure, and manage your own software—including operating systems, middleware, and applications.
Lift-and-shift migration
This is the fastest and least expensive method of migrating an application or workload to the cloud. Without refactoring your underlying architecture, you can increase the scale and performance, enhance the security, and reduce the costs of running an application or workload.
Test and development
Your team can quickly set up and dismantle test and development environments, bringing new applications to market faster. IaaS makes it quick and economical to scale dev/test environments up and down.
Storage, backup, and recovery
Your organization avoids the capital outlay for storage and the complexity of storage management, which typically requires a skilled staff to manage data and meet legal and compliance requirements. IaaS is useful for handling unpredictable demand and steadily growing storage needs. It also can simplify planning and management of backup and recovery systems.
Web apps
IaaS provides all the infrastructure to support web apps, including storage, web and application servers, and networking resources. Your organization can quickly deploy web apps on IaaS and easily scale infrastructure up and down when demand for the apps is unpredictable.
High-performance computing
High-performance computing on supercomputers, computer grids, or computer clusters helps solve complex problems involving millions of variables or calculations. Examples include protein folding and earthquake simulations, climate and weather predictions, financial modeling, and product design evaluations.
Advantages of IaaS
Reduces capital expenditures and optimizes costs
IaaS eliminates the cost of configuring and managing a physical datacenter, which makes it a cost-effective choice for migrating to the cloud. The pay-as-you-go subscription models used by IaaS providers help you reduce hardware costs and maintenance and enable your IT team to focus on core business.
Increases scale and performance of IT workloads
IaaS lets you scale globally and accommodate spikes in resource demand. That way, you can deliver IT resources to employees from anywhere in the world faster and enhance application performance.
Increases stability, reliability, and supportability
With IaaS, there’s no need to maintain and upgrade software and hardware or troubleshoot equipment problems. With the appropriate agreement in place, the service provider assures that your infrastructure is reliable and meets service-level agreements (SLAs).
Improves business continuity and disaster recovery
Achieving high availability, business continuity, and disaster recovery is expensive because it requires a significant amount of technology and staff. But with the right SLA in place, IaaS helps to reduce this cost. It also helps you access applications and data as usual during a disaster or outage.
Enhances security
With the appropriate service agreement, a cloud service provider can offer better security for your applications and data than the security you would attain in house.
Helps you innovate and get new apps to users faster
With IaaS, once you’ve decided to launch a new product or initiative, the necessary computing infrastructure can be ready in minutes or hours, rather than in days or weeks. And because you don’t need to set up the underlying infrastructure, IaaS lets you deliver your apps to users faster.
IaaS platform and architecture
IaaS is made up of a collection of physical and virtualized resources that provide consumers with the basic building blocks needed to run applications and workloads in the cloud.
Physical data centers: IaaS providers will manage large data centers, typically around the world, that contain the physical machines required to power the various layers of abstraction on top of them and that are made available to end users over the web. In most IaaS models, end users do not interact directly with the physical infrastructure, but it is provided as a service to them.
Compute: IaaS is typically understood as virtualized compute resources, so for the purposes of this article, we will define IaaS compute as a virtual machine. Providers manage the hypervisors and end users can then programmatically provision virtual “instances” with desired amounts of compute and memory (and sometimes storage). Most providers offer both CPUs and GPUs for different types of workloads. Cloud compute also typically comes paired with supporting services like auto scaling and load balancing that provide the scale and performance characteristics that make cloud desirable in the first place.
Network: Networking in the cloud is a form of Software Defined Networking in which traditional networking hardware, such as routers and switches, are made available programmatically, typically through APIs. More advanced networking use cases involve the construction of multi-zone regions and virtual private clouds, both of which will be discussed in more detail later.
Storage: The three primary types of cloud storage are block storage, file storage, and object storage. Block and file storage are common in traditional data centers but can often struggle with scale, performance and distributed characteristics of cloud. Thus, of the three, object storage has thus become the most common mode of storage in the cloud given that it is highly distributed (and thus resilient), it leverages commodity hardware, data can be accessed easily over HTTP, and scale is not only essentially limitless but performance scales linearly as the cluster grows.
Read More About ITIL
Buy From Amazon
